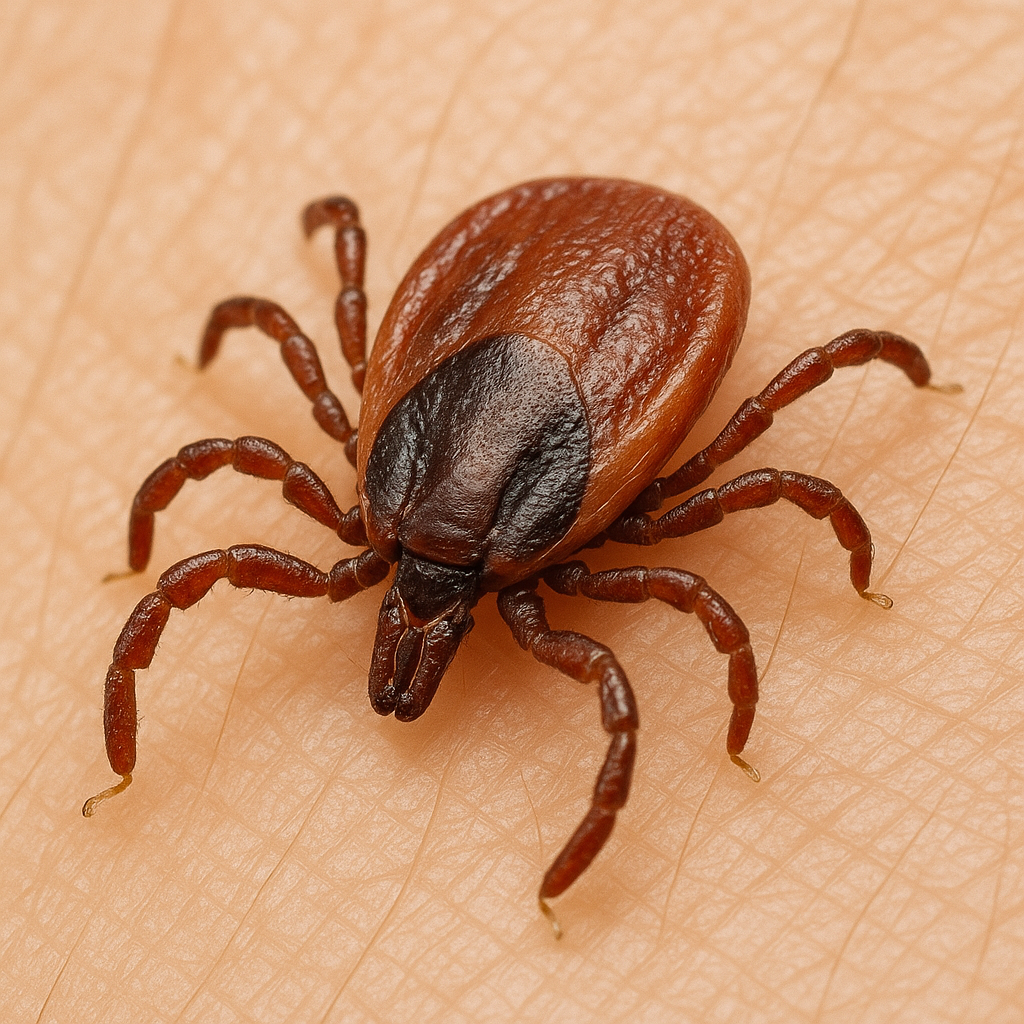
Understanding Lyme Disease
Your Guide to Lyme Disease Awareness
Explore the causes, symptoms, and prevention of Lyme disease to protect yourself and your loved ones.
About Lyme Disease
Symptoms of Lyme Disease
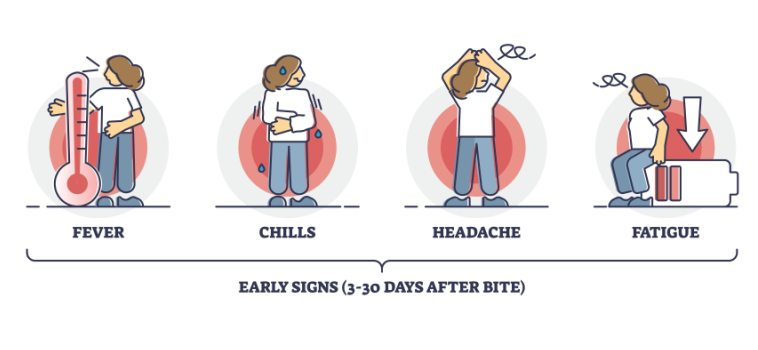
Early Symptoms
In the initial stage, symptoms may include fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes, often accompanied by a characteristic ‘bull’s-eye’ skin rash.
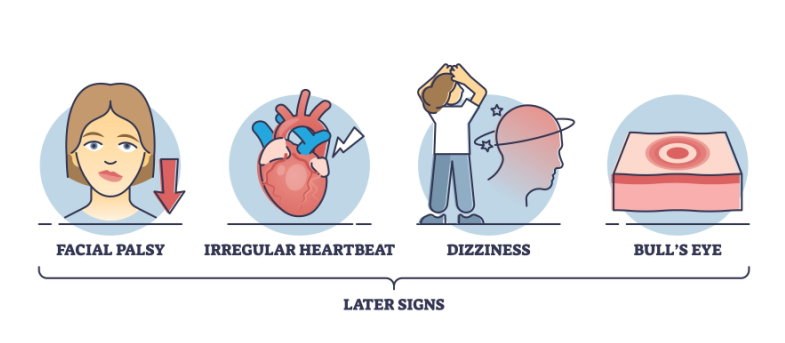
Later Symptoms
If untreated, the infection can spread to the joints, heart, and nervous system, leading to severe headaches, neck stiffness, arthritis with severe joint pain and swelling, facial palsy, and irregular heartbeats. There can also be mood and emotional changes.
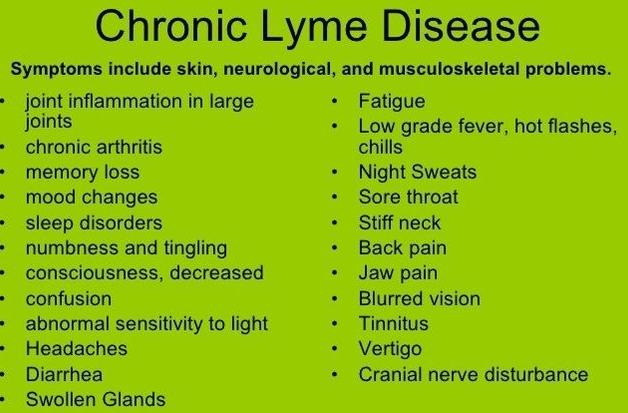
Chronic Symptoms
In some cases, Lyme disease can cause long-term symptoms such as cognitive difficulties, fatigue, and chronic pain, even after treatment. These persistent symptoms are often referred to as Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS).
Symptoms and Signs of Lyme Disease
Overview
Lyme disease is known for its protean manifestations—a wide variety of possible signs and symptoms. Because Borrelia burgdorferi can infect nearly any organ or tissue, Lyme may mimic other conditions. It should be considered in the differential diagnosis of:
-
Rheumatologic diseases
-
Neurologic disorders
-
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS)
-
Fibromyalgia
-
Somatization disorder
-
Other complex multi-system illnesses
Common Symptoms and Signs of Early Lyme Disease
-
Erythema Migrans (EM) rash – hallmark expanding skin lesion (though not always present)
-
Fatigue, malaise
-
Flu-like illness – fever, headache, joint and muscle aches
-
Stiff neck
-
Dysesthesia – abnormal sensations
-
Lymphadenopathy – swollen lymph nodes
-
Facial nerve dysfunction – weakness/paralysis of facial muscles (often mislabeled as Bell’s palsy)
Common Symptoms and Signs of Disseminated and Late Lyme Disease
-
Persistent fatigue
-
Multiple EM rashes (in some cases)
-
Severe headaches and neck stiffness
-
Arthritis – joint swelling and/or pain
-
Neuropathic symptoms – nerve pain, tingling, numbness, hot/cold sensations
-
Cognitive dysfunction – difficulty concentrating, “brain fog”
-
Memory impairment
-
Unprovoked pain (often disrupting sleep)
-
Cardiac symptoms – palpitations, chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting
-
Gastrointestinal issues
-
Neuropsychiatric symptoms – depression, anxiety, mood changes
Lyme disease can significantly affect a person’s emotional state, both directly and indirectly. The emotional impact is often tied to the neurological effects of the disease as well as the challenges of living with a chronic illness.

Direct Neurological Effects on Emotional State
The bacteria that cause Lyme disease, Borrelia burgdorferi, can directly impact the central nervous system, leading to changes in a person’s emotional and psychological well-being. This is a part of neuroborreliosis, where the infection causes inflammation in the brain.
- Mood Swings: Patients often report uncharacteristic irritability, anger, and sudden changes in mood.
- Anxiety and Panic Attacks: The neurological effects can trigger heightened anxiety or panic attacks, which may be new experiences for the individual.
- Depression: Lyme disease has been linked to depression, which can range from a persistent low mood to severe depressive episodes. This is thought to be a result of the inflammatory processes affecting brain regions that regulate mood.
- Cognitive Difficulties: The “brain fog” and memory issues associated with the disease can be a source of significant frustration and distress, leading to feelings of sadness, anxiety, and a loss of confidence.

Indirect Emotional Effects from Living with a Chronic Illness
Beyond the direct neurological impact, the emotional toll of Lyme disease is also a result of the challenges of living with a chronic and often misunderstood illness.
- Frustration and Isolation: The debilitating physical symptoms—such as chronic pain, fatigue, and joint swelling—can prevent a person from engaging in their usual activities, leading to a sense of isolation and frustration. Friends and family may not fully understand the invisible nature of the illness, which can make a person feel misunderstood and alone.
- Stress and Uncertainty: The diagnostic process for Lyme disease can be long and difficult, often involving multiple doctor visits and misdiagnoses. The uncertainty of a diagnosis and the unpredictable nature of the symptoms can be a major source of stress.
- Loss of Identity: A person’s identity is often tied to their work, hobbies, and social roles. When Lyme disease disrupts these parts of their life, it can lead to a feeling of loss and a difficult adjustment to a new normal.
- Grief: It’s not uncommon for people with Lyme disease to experience a form of grief for the life they had before the illness. This can include grieving for their health, their career, their physical abilities, and their relationships.
Treatment Options for Lyme Disease
Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotic therapy is the primary treatment for Lyme disease, especially effective when administered in the early stages of infection. It helps eliminate the bacteria and prevent further complications.
Symptom Management
In addition to antibiotics, managing symptoms such as pain and inflammation is crucial. This may involve the use of pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications.
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up care ensures that the treatment is effective and helps monitor for any potential long-term effects or recurrence of symptoms.
Preventing Lyme Disease
Effective Tick Bite Prevention
Preventing Lyme disease starts with avoiding tick bites. Wear protective clothing, use insect repellent, and perform regular tick checks after spending time in wooded or grassy areas. Keeping your yard tidy and using tick control products can also reduce the risk of tick exposure.
Common Questions About Lyme Disease
Understanding Lyme disease is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you stay informed.
What are the early symptoms of Lyme disease?
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
Can Lyme disease be cured?
What happens if Lyme disease is left untreated?
Is there a vaccine for Lyme disease?
How can I protect my pets from Lyme disease?
Take Charge of Your Health
If you suspect Lyme disease, don’t wait. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Explore our resources or consult a healthcare professional today to ensure your well-being.
